Etching is the process of cutting into unprotected portions of a metal surface using a strong acid to create an intaglio design (creating an image by cutting, engraving, or engraving into a flat surface) in the metal. As a method of intaglio printmaking, it is, like engraving, the most important technique of old original printmaking and is still widely used today.
In pure etching, a metal (usually copper, zinc, or steel) plate is covered with an acid-resistant, waxy underlayer. The artist then uses a sharp etching needle to scrape away the lines on the ground that he or she wants to appear in the finished product, thus exposing the bare metal. The plate is then dipped in an acid bath. The acid “erodes” the exposed metal, leaving lines that sink into the sheet metal. Then clean the remaining grounds off the plate. The printing plate is filled with ink, and then the ink is wiped off the surface, leaving only the ink on the etched lines.
The plate is then put into a high-pressure press along with a sheet of paper (usually moistened to soften it). The paper picks up the ink from the etched lines, creating a print. This process can be repeated many times; typically several hundred impressions can be printed before the plate shows too much wear. Work on the plate can also be added by repeating the whole process; this creates an etch that exists in multiple states. Etching is often combined with other intaglio techniques such as engraving or watercolour.
The Manufacturing Process Of Etching
Firstly, the pattern to be etched is transferred to the film film by silk screen printing, or transferred to the glass film by photolithography, and then the film is aligned by manual alignment or machine alignment. Then place the steel sheet coated with photosensitive ink or pasted with photosensitive dry film under the film, and then expose it to ultraviolet light after inhaling. When exposed, the steel sheet corresponding to the black part of the film (etched pattern) is not photosensitive, and the steel sheet corresponding to the white part of the film is photosensitive, and the ink or dry film on the photosensitive part of the steel sheet undergoes a polymerization reaction. Finally, through the developing machine, the photosensitive ink or dry film on the steel sheet is not melted by the developer, while the unphotosensitive ink or dry film is melted and removed by the developer, so that the pattern to be etched is transferred to the steel sheet after exposure and development up.
Digression: In fact, the exposure and development process can also be applied to the production of some metal shell logos, such as the highlighted logo of the aluminum alloy mobile phone shell below.
Approximate process flow: Shell polishing—spray photosensitive ink—exposure and development—remove non-protected area ink (non-logo area)—sandblasting—first anodizing and dyeing—radium carving out conductive potential— Secondary oxidation, dyeing (if the logo area needs color).
Compared with other mechanical processing techniques, metal etching mainly has the following advantages:
- Low mold opening fee, can be changed arbitrarily according to the design requirements of the designer, flexible changes, low cost, and short template production cycle.
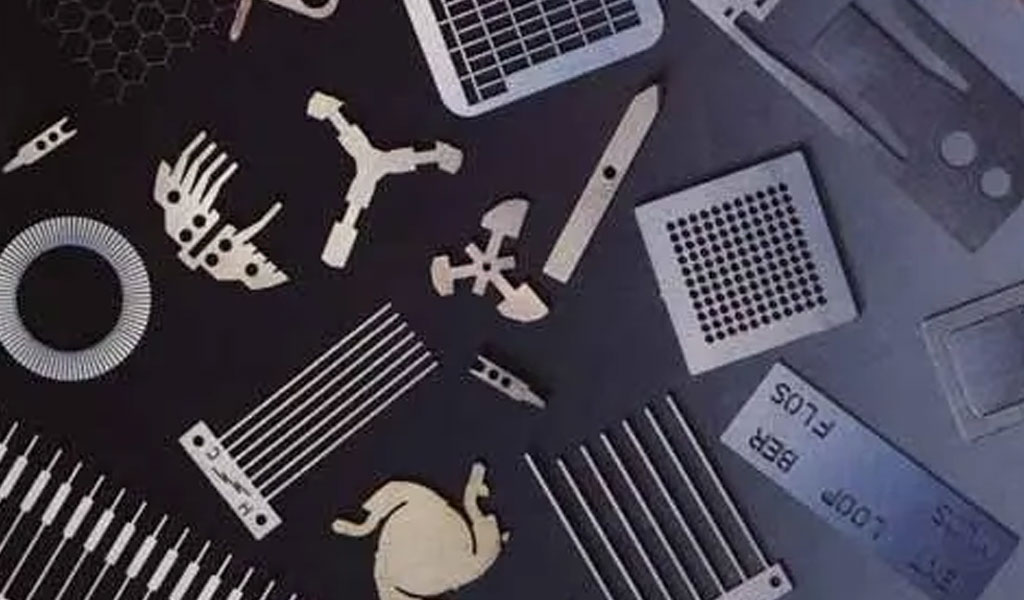
- The etching pattern has great adaptability, and there are no restrictions on various pattern designs. For particularly fine patterns, the etching process can even provide better results, and can also realize half-etching of the metal surface.
- High precision, up to +/-0.01mm precision, meeting the assembly requirements of different products, the thinner the material, the higher the precision control. It can process the thinnest 0.02mm thick metal material, up to 1mm thick, and can realize mass production and processing.
- High processing quality, no burrs, pressure points, no deformation of the product, no change of material properties, no influence on the function of the product. Especially for products with surface assembly requirements and smoothness requirements, etching processing solves various shortcomings of stamping, wire cutting and laser cutting processing.
- At the same time, the accuracy can meet the requirements of the product, even better than the above-mentioned several processes, and has irreplaceability.
- Almost all metals can be etched, and different metal materials need to be equipped with different chemical formulas. For example: rare metals: molybdenum, etc., can also be etched.
- It is easy to manufacture metal parts that are difficult to process by other mechanical processing methods. Stamping and laser can not complete fine, ultra-thin material processing, and etching is easier to deal with.
Pay Attention To The Problem

1. Reduce side erosion and edge, improve etching coefficient
The side erosion produces a ledge. Generally, the longer the printed board is in the etching solution, the more serious the side etching will be. Side etching seriously affects the accuracy of printed wires, and severe side etching will make it impossible to make fine wires. When the side etching and the edge are reduced, the etching coefficient increases, and a high etching coefficient indicates the ability to maintain thin wires, so that the etched wires are close to the size of the original image. Plating Etch Resist Whether tin-lead alloy, tin, tin-nickel alloy or nickel, excessive beading will cause short circuit in the wire. Because the protruding edge breaks off easily, an electrical bridge is formed between the two points of the wire.
There are many factors that affect side erosion, some of which are outlined below:
- Etching method: Soaking and bubbling etching will cause larger side erosion, while splash and spray etching will cause smaller side erosion, especially spray etching has the best effect.
- Types of etching solutions: different etching solutions have different chemical components, their etching rates are different, and their etching coefficients are also different. For example: the etching coefficient of acidic copper chloride etching solution is usually 3, and the etching coefficient of alkaline copper chloride etching solution can reach 4. Recent studies have shown that nitric acid-based etching systems can achieve almost no undercutting, and the sidewalls of etched lines are nearly vertical. Such etching systems are under development.
- Etching rate: slow etching rate will cause serious side erosion. The improvement of etching quality has a lot to do with the acceleration of etching rate. The faster the etching speed, the shorter the time the board stays in the etching solution, the smaller the amount of side etching, and the etched graphics are clear and tidy.
- The pH value of the etching solution: When the pH value of the alkaline etching solution is higher, the side etching increases. See Figure 10-3. In order to reduce side erosion, the general pH value should be controlled below 8.5.
- Density of etching solution: If the density of alkaline etching solution is too low, it will aggravate side corrosion, see Figure 10-4. It is beneficial to use high copper concentration etching solution to reduce side corrosion.
- Thickness of copper foil: For the etching of thin wires with minimum side etching, it is best to use (ultra) thin copper foil. And the thinner the line width,
The thickness of copper foil should be thinner. Because the thinner the copper foil, the shorter the time in the etching solution, and the smaller the amount of side etching.
2. Improve the consistency of etch rate between boards
In continuous board etching, the more consistent the etch rate, the more uniformly etched boards can be obtained. To meet this requirement, it is necessary to ensure that the etching solution is always kept in the best etching state during the whole etching process. This requires the selection of an etching solution that is easy to regenerate and compensate, and the etching rate is easy to control. Select processes and equipment that can provide constant operating conditions and automatically control various solution parameters. It is realized by controlling the pH value of the solution, the concentration of the solution, the temperature, the uniformity of the solution flow (the spray system or the nozzle and the swing of the nozzle), etc.
3. Improve the uniformity of etching rate on the entire board surface
The etching uniformity of the upper and lower sides of the board and various parts on the board is determined by the uniformity of the etchant flow on the board surface.
During the etching process, the etching rates of the upper and lower surfaces are often inconsistent. Generally, the etch rate of the lower side is higher than that of the upper side. Because there is accumulation of solution on the upper surface, the progress of etching reaction is weakened. The phenomenon of uneven etching on the upper and lower plates can be solved by adjusting the spray pressure of the upper and lower nozzles. A common problem with etching printed boards is that it is difficult to etch the entire surface of the board in the same time. The edges of the board are etched faster than the center of the board. Using a sprinkler system and oscillating the nozzles is an effective measure. Further improvement can be achieved by making the spray pressure at the center of the board and the edge of the board different, and intermittently etching the front end of the board and the rear end of the board to achieve etching uniformity on the entire board surface.
Laser Engraving VS Etching
Laser marking is the use of laser beams to make permanent marks on the surface of various materials. The marking effect of the laser marking machine is to expose the deep material through the evaporation of the surface material, or to “carve” traces through the chemical and physical changes of the surface material through the light energy, or to burn part of the material through the light energy, showing the The patterns and characters to be etched are high-precision engraving: the laser marking machine marks clearly, permanently and beautifully. The engraved items have fine patterns, and the line width can reach 0.04mm. Moreover, a large amount of data can be printed on a very small plastic part. Persistence: Changes in the environment (touch, acid and reducing gas, high temperature, low temperature, etc.) will not make the marking fade away.
What is the difference between engraving and etching of a laser marking:
- The principle is different: generally speaking, laser engraving uses the burning of the laser beam to vaporize the surface of the medium, while etching uses the redox reaction between substances to dissolve the metal.
- The effect is different: as far as the current technology is concerned, laser engraving cannot achieve deep engraving for many metal media and some denser substances, often the depth is very shallow and cannot meet the speed requirements, while the depth of metal etching can basically be achieved. It can be done as you like, and it can be combined with the painting process to achieve multi-colored and multi-colored decoration.
- The scope of application is different: laser engraving has a wider application scope, and most media can be laser engraved or marked, while etching is limited to metal or stone.
- The process flow is different: the laser engraving process is simple and the process is less. However, there are more etching processes and more details.
- The production efficiency is different: laser engraving is suitable for small batch engraving or marking, while etching process is more suitable for mass production.
- The precision is different: Generally speaking, the precision of the etching process is higher. Combined with the photoresist process, it is not a problem to achieve a line of 0.01 mm.